What Is a Port Logistics
What is port logistics and why is it important?
Port logistics encompasses the intricate processes and systems involved in managing the movement of goods through seaports. It is a critical component of global trade, facilitating the efficient transfer of cargo between ships, trucks, and trains. Port logistics ensures that goods arrive at their destination on time, in good condition, and at a reasonable cost.

The importance of port logistics cannot be overstated. It plays a vital role in the global supply chain, connecting producers and consumers across continents. By streamlining the movement of goods, port logistics helps to reduce transportation costs, minimize delays, and improve overall supply chain efficiency. This, in turn, benefits businesses, consumers, and the economy as a whole.
Moreover, port logistics is a significant contributor to economic growth. It creates jobs, generates revenue for local governments, and supports the development of related industries such as warehousing, distribution, and logistics services. Efficient port logistics can also enhance a country’s competitiveness in the global market, making it an attractive destination for foreign investment and trade.
How does the port logistics process work?
The port logistics process involves a series of interconnected steps that ensure the smooth movement of goods through the port. Here’s a breakdown of the key stages:
Cargo arrival and unloading
When a ship arrives at the port, the cargo must be unloaded in a timely and efficient manner. This process involves the use of specialized equipment such as cranes, forklifts, and straddle carriers to transfer the goods from the ship to the port’s storage facilities or directly onto waiting trucks or trains.
Storage and handling
Once the cargo has been unloaded, it is transported to designated storage areas within the port. These storage facilities, which may include warehouses, container yards, and silos, are designed to protect the goods from the elements and ensure their safe keeping until they are ready for onward transportation.
Customs clearance
Before the cargo can leave the port, it must undergo customs clearance. This process involves the submission of required documentation, such as invoices, packing lists, and bills of lading, to customs authorities. The goods may also be subject to inspection to ensure compliance with import and export regulations.
Onward transportation
After the cargo has been cleared by customs, it is loaded onto trucks or trains for onward transportation to its final destination. The choice of transportation mode depends on factors such as the type of goods, the distance to be traveled, and the urgency of delivery.
Coordination and communication
Throughout the port logistics process, effective coordination and communication are essential. This involves the exchange of information between various stakeholders, including shipping lines, terminal operators, customs authorities, and transportation providers. The use of technology, such as electronic data interchange (EDI) and port community systems, helps to streamline communication and improve overall efficiency.
What infrastructure and equipment are essential for port logistics?
Efficient port logistics requires a range of infrastructure and equipment to support the various processes involved. Some of the key components include:
Berths and wharves
Berths and wharves are the areas within the port where ships dock and unload their cargo. They are designed to accommodate different types of ships, from container vessels to bulk carriers, and must be equipped with the necessary infrastructure to facilitate the loading and unloading process.
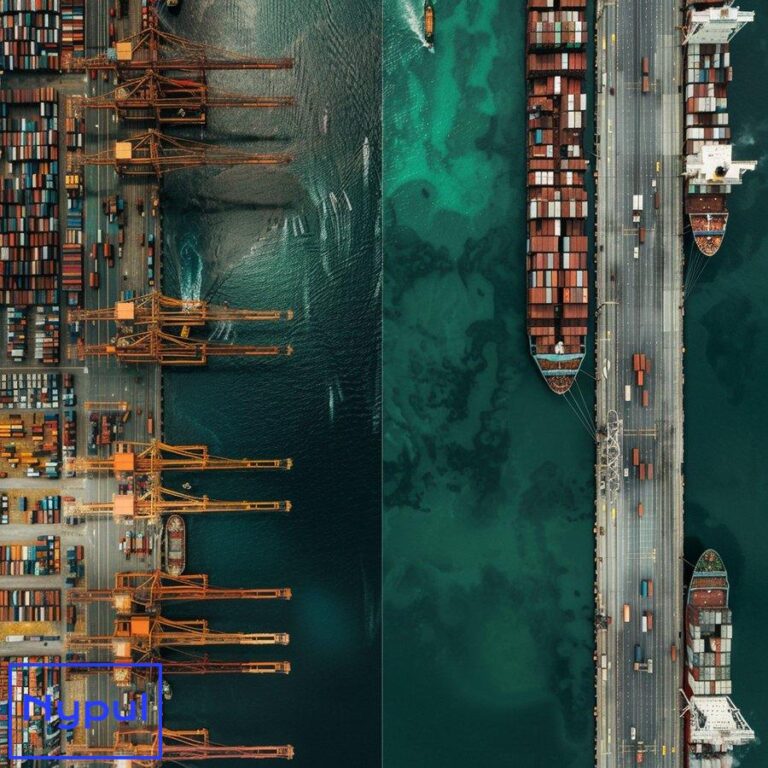
Container terminals
Container terminals are specialized facilities within the port that handle the movement of containerized cargo. They typically include container yards for storage, gantry cranes for loading and unloading containers, and specialized equipment for stacking and moving containers within the terminal.
Warehouses and storage facilities
Warehouses and storage facilities are essential for the safe keeping of goods until they are ready for onward transportation. These facilities must be designed to protect the goods from the elements and ensure their security.
Intermodal facilities
Intermodal facilities are areas within the port where cargo can be transferred between different modes of transportation, such as ships, trains, and trucks. These facilities typically include rail yards, truck terminals, and specialized equipment for loading and unloading cargo.
Information technology
Information technology plays a crucial role in port logistics, enabling the efficient exchange of information between various stakeholders. This includes systems for tracking cargo, managing inventory, and coordinating transportation.
Specialized equipment
Specialized equipment, such as cranes, forklifts, and straddle carriers, is essential for the loading and unloading of cargo. These machines must be well-maintained and operated by trained personnel to ensure safety and efficiency.
What are the main challenges in port logistics?
Port logistics faces a number of challenges that can impact the efficiency and effectiveness of the supply chain. Some of the key challenges include:
Congestion and delays
Congestion and delays are common problems in port logistics, particularly during peak periods or when there are disruptions to the supply chain. These issues can lead to increased costs, lost productivity, and dissatisfied customers.
Security and safety
Ensuring the security and safety of cargo, personnel, and infrastructure is a critical challenge in port logistics. Ports must implement robust security measures to prevent theft, vandalism, and terrorist attacks, while also ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
Environmental impact
The movement of goods through ports can have a significant impact on the environment, particularly in terms of air pollution, noise pollution, and the potential for oil spills or other hazardous materials incidents. Ports must balance the need for efficient operations with the need to minimize their environmental footprint.
Technological challenges
Keeping up with the latest technological developments in port logistics can be a challenge, particularly for smaller ports with limited resources. Implementing new technologies can be costly and time-consuming, and there may be resistance to change among some stakeholders.
Regulatory compliance
Ports must comply with a complex web of regulations governing everything from customs clearance to environmental protection. Failure to comply can result in fines, delays, and reputational damage.
Labor issues
Labor issues, such as strikes, disputes over working conditions, and skills shortages, can disrupt port operations and impact the supply chain. Ports must work closely with labor unions and training providers to ensure a stable and skilled workforce.
How do innovations impact port logistics operations?
Innovations in technology and processes are transforming the way that port logistics operations are conducted. Some of the key innovations include:
Automation and robotics
The use of automation and robotics is becoming increasingly common in port logistics, with the potential to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance safety. Examples include automated container terminals, where cranes and straddle carriers are operated remotely or autonomously, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) for moving cargo within the terminal.
Data analytics and artificial intelligence
Data analytics and artificial intelligence are being used to optimize port logistics operations, from predicting demand and optimizing resource allocation to identifying potential bottlenecks and inefficiencies. By leveraging data from various sources, including sensors, tracking systems, and historical records, ports can make more informed decisions and improve overall performance.
Blockchain technology
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the way that information is shared and transactions are conducted in port logistics. By creating a secure, decentralized ledger of transactions, blockchain can help to reduce paperwork, improve transparency, and enhance trust between stakeholders.
Sustainability initiatives
Ports are increasingly focused on implementing sustainability initiatives to reduce their environmental impact and promote more sustainable practices throughout the supply chain. This includes investments in renewable energy, alternative fuels, and waste management systems, as well as initiatives to promote modal shift from road to rail or inland waterways.
Collaboration and partnerships
Collaboration and partnerships between ports, shipping lines, terminal operators, and other stakeholders are essential for driving innovation and improving overall efficiency. By sharing best practices, pooling resources, and working towards common goals, stakeholders can achieve more than they could individually.
What economic benefits does port logistics bring?

Port logistics plays a critical role in driving economic growth and development. Some of the key economic benefits include:
Job creation
Port logistics creates a significant number of direct and indirect jobs, ranging from dock workers and truck drivers to logistics managers and IT professionals. These jobs provide employment opportunities for local communities and contribute to economic prosperity.
Revenue generation
Ports generate revenue through a variety of channels, including fees for dockage, wharfage, storage, and other services. This revenue helps to fund infrastructure improvements, support local government budgets, and attract further investment to the region.
Trade facilitation
By facilitating the movement of goods through the supply chain, port logistics helps to promote trade and economic integration. This can lead to increased exports, reduced costs for consumers, and greater access to global markets for businesses.
Multiplier effects
The economic benefits of port logistics extend beyond the port itself, with multiplier effects rippling through the local and regional economy. Businesses that rely on the port for their supply chains may choose to locate nearby, creating additional jobs and investment opportunities.
Competitiveness
Efficient port logistics can enhance a country’s competitiveness in the global market, making it an attractive destination for foreign investment and trade. This can lead to increased economic growth, job creation, and prosperity.
How does port logistics differ from other types of logistics?
While port logistics shares many similarities with other types of logistics, such as warehousing and transportation, there are some key differences:

Scale and complexity
Port logistics involves the movement of large volumes of cargo through a complex network of facilities, equipment, and stakeholders. This scale and complexity requires specialized knowledge, skills, and infrastructure that may not be necessary in other types of logistics.
Intermodal transportation
Port logistics often involves the use of multiple modes of transportation, such as ships, trains, and trucks, to move goods from origin to destination. This intermodal approach requires specialized equipment and coordination to ensure seamless transitions between modes.
Customs and regulatory requirements
Ports are subject to a range of customs and regulatory requirements that may not apply to other types of logistics. This includes compliance with import and export regulations, customs clearance procedures, and security measures.
Environmental considerations
The movement of goods through ports can have a significant impact on the environment, particularly in terms of air pollution, noise pollution, and the potential for oil spills or other hazardous materials incidents. Ports must balance the need for efficient operations with the need to minimize their environmental footprint.
Stakeholder coordination
Port logistics involves a wide range of stakeholders, including shipping lines, terminal operators, customs authorities, transportation providers, and government agencies. Effective coordination and communication between these stakeholders is essential for ensuring the smooth flow of goods through the supply chain.
What can we learn from successful port logistics case studies?
Successful port logistics case studies offer valuable insights into best practices and strategies for improving efficiency and effectiveness. Here are a few examples:

Port of Rotterdam, Netherlands
The Port of Rotterdam has implemented a range of innovative technologies and processes to improve its logistics operations. This includes the use of automated container terminals, data analytics to optimize resource allocation, and blockchain technology to streamline information sharing and transactions. The port has also invested heavily in sustainability initiatives, such as the use of shore power for ships and the development of a circular economy park.
Port of Los Angeles, United States
The Port of Los Angeles has taken a proactive approach to addressing the challenge of congestion and delays. This includes the implementation of a “container dwell fee” to incentivize the timely removal of containers from the port, and the use of data analytics to identify potential bottlenecks and inefficiencies. The port has also worked closely with stakeholders to promote the use of off-peak hours and reduce truck idling times.
Port of Singapore, Singapore
The Port of Singapore is known for its efficiency and innovation. It has implemented a range of technologies to optimize its logistics operations, including automated guided vehicles (AGVs) for moving containers within the terminal and a port community system to facilitate information sharing between stakeholders. The port has also invested heavily in sustainability initiatives, such as the use of liquefied natural gas (LNG) as a fuel for its ships and the development of a smart grid to manage energy consumption.
These case studies demonstrate the importance of innovation, collaboration, and sustainability in driving success in port logistics. By embracing new technologies, promoting stakeholder coordination, and prioritizing environmental considerations, ports can improve their efficiency, competitiveness, and economic impact.