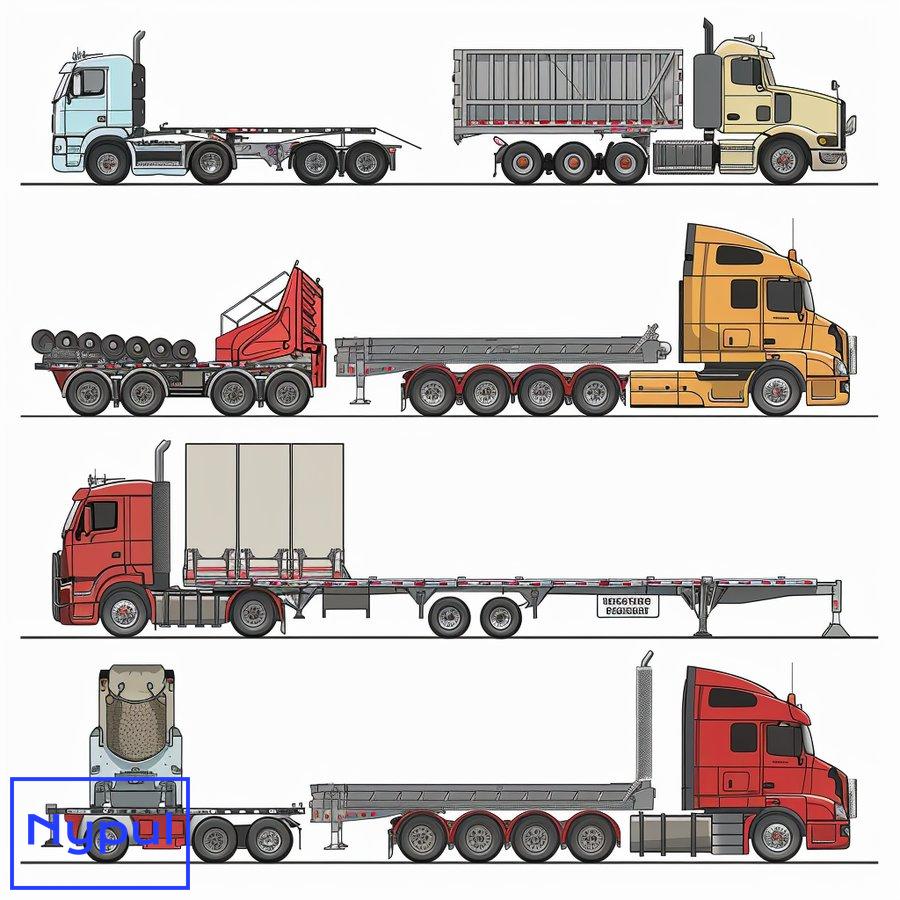
What Kind of Trailer Hauls Heavy Equipment
Heavy equipment transport is a critical component of various industries, including construction, mining, agriculture, and manufacturing. The success of these operations often hinges on the ability to move large, heavy machinery from one location to another safely and efficiently. Selecting the right trailer for hauling heavy equipment is crucial, as it directly impacts the safety, legality, and cost-effectiveness of the transport operation.
What are the main types of trailers used for hauling heavy equipment?
The heavy equipment transport industry relies on several specialized trailer types to move machinery and oversized loads. Each trailer type is designed to accommodate specific weight capacities, dimensions, and load configurations. Understanding the characteristics and capabilities of these trailers is essential for anyone involved in heavy equipment logistics.
Lowboy Trailers
Lowboy trailers, also known as low-bed or double-drop trailers, are characterized by their low deck height, typically ranging from 18 to 24 inches off the ground. This low profile allows for the transport of tall equipment while staying within legal height limits. Lowboys are versatile and can handle a wide range of heavy machinery, including excavators, bulldozers, and large industrial equipment.
Flatbed Trailers
Flatbed trailers feature a flat, level deck without sides or a roof. They offer flexibility in loading and unloading from multiple angles. While not specifically designed for heavy equipment, flatbeds can accommodate certain types of machinery, especially those with lower profiles or when used with additional equipment like ramps.
Step Deck Trailers
Step deck trailers, also called drop deck trailers, have two deck levels. The lower deck provides additional vertical clearance for taller equipment. The “step” design allows for easier loading and unloading compared to traditional flatbeds, making them suitable for various types of heavy machinery.
Removable Gooseneck (RGN) Trailers
RGN trailers feature a detachable front section that lowers the deck to ground level, creating a built-in ramp for easy loading. These trailers are ideal for equipment that can be driven or rolled onto the deck, such as large tractors or mobile cranes.
Double Drop Trailers
Double drop trailers have a well in the middle section that sits lower than the front and rear decks. This design allows for the transport of extremely tall equipment while maintaining legal height restrictions. Double drops are often used for hauling oversized industrial machinery or construction equipment.
Specialized Trailers
Various specialized trailers cater to specific types of heavy equipment or unique transport requirements. These may include:
- Beam trailers for extremely long loads
- Multi-axle trailers for distributing weight over more axles
- Extendable trailers for adjustable length capabilities
The selection of the appropriate trailer type depends on factors such as the equipment’s weight, dimensions, loading method, and transport route. Each trailer type offers distinct advantages and limitations, making it crucial to match the trailer to the specific requirements of the heavy equipment being transported.
How do weight capacity and dimensions affect trailer selection?

Weight capacity and dimensions are critical factors in selecting the appropriate trailer for heavy equipment transport. These parameters not only determine the feasibility of moving a particular piece of machinery but also impact legal compliance, safety, and operational efficiency.
Weight Capacity Considerations
The weight capacity of a trailer, often referred to as its payload capacity, is the maximum weight it can safely carry. This capacity is influenced by several factors:
- Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR): The maximum weight of the fully loaded trailer, including the weight of the trailer itself.
- Axle configuration: The number and arrangement of axles affect weight distribution and overall capacity.
- Trailer construction: The materials and design of the trailer impact its strength and load-bearing capabilities.
When selecting a trailer, it’s crucial to consider not only the weight of the equipment but also any additional items that will be transported, such as attachments or accessories. A safety margin should always be maintained to account for unexpected weight variations or road conditions.
Dimensional Considerations
The dimensions of both the equipment and the trailer play a significant role in transport planning:
- Length: Affects maneuverability, turning radius, and compliance with road regulations.
- Width: Determines whether the load is considered oversized and requires special permits.
- Height: Crucial for clearance under bridges, overpasses, and power lines.
Trailer selection must account for the equipment’s dimensions in all three axes. For example, a piece of equipment that is particularly tall may require a lowboy trailer to stay within legal height limits, while an exceptionally long item might necessitate an extendable trailer.
Legal and Regulatory Impact
Weight and dimensional limits are strictly regulated on public roads. Exceeding these limits can result in:
- Requirement for special permits
- Restricted travel routes
- Mandatory escort vehicles
- Hefty fines and penalties
Proper trailer selection ensures compliance with these regulations, avoiding costly delays and legal issues.
Operational Efficiency
Matching the trailer to the equipment’s weight and dimensions optimizes operational efficiency:
- Proper weight distribution improves vehicle handling and fuel efficiency.
- Appropriate dimensional fit reduces the need for complex loading procedures.
- Correct trailer selection minimizes the risk of equipment damage during transport.
Load Distribution
Proper load distribution is essential for safe and legal transport. The weight of the equipment must be distributed evenly across the trailer’s axles to ensure stability and compliance with axle weight limits. Some trailers, such as those with sliding axles or adjustable goosenecks, allow for fine-tuning of weight distribution.
| Trailer Type | Typical Weight Capacity | Common Dimensions (L x W) | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lowboy | 40,000 – 80,000 lbs | 48′ – 53′ x 8’6″ | Tall, heavy equipment |
| Flatbed | 48,000 – 60,000 lbs | 48′ – 53′ x 8’6″ | Versatile loads |
| Step Deck | 48,000 – 60,000 lbs | 48′ – 53′ x 8’6″ | Medium-height equipment |
| RGN | 50,000 – 150,000+ lbs | 48′ – 65’+ x 8’6″ – 10′ | Heavy, self-loading equipment |
| Double Drop | 40,000 – 80,000 lbs | 40′ – 50′ x 8’6″ | Extra tall equipment |
This table provides a general overview of typical weight capacities and dimensions for common heavy equipment trailers. However, it’s important to note that these figures can vary significantly based on specific trailer models and configurations.
In conclusion, weight capacity and dimensions are fundamental considerations in trailer selection for heavy equipment transport. A thorough understanding of these factors ensures safe, legal, and efficient transportation of machinery, ultimately contributing to the success of projects across various industries.
Why are lowboy trailers considered the workhorses of heavy equipment transport?
Lowboy trailers have earned the reputation as the workhorses of heavy equipment transport due to their versatility, efficiency, and ability to handle a wide range of challenging loads. These trailers are specifically designed to address the unique requirements of transporting large, heavy machinery while maintaining compliance with road regulations.
Design and Structure
The defining feature of a lowboy trailer is its low deck height, typically ranging from 18 to 24 inches off the ground. This design consists of three main sections:
- The front deck (also called the gooseneck)
- The main deck (the lowered section)
- The rear deck (which may include a beaver tail for easier loading)
This structure allows for the transportation of tall equipment while staying within legal height limits, which is typically 13’6″ to 14′ in most jurisdictions.
Versatility in Load Types
Lowboy trailers can accommodate a diverse range of heavy equipment:
- Construction machinery: Excavators, bulldozers, wheel loaders
- Industrial equipment: Large generators, industrial boilers, manufacturing machinery
- Agricultural equipment: Combine harvesters, large tractors
- Mining equipment: Haul trucks, drilling rigs
The ability to handle such a wide variety of equipment makes lowboys indispensable in multiple industries.
Weight Capacity
Lowboy trailers are engineered to carry substantial loads:
- Standard lowboys typically have a capacity of 40,000 to 80,000 pounds.
- Heavy-duty models can handle loads exceeding 100,000 pounds.
This high weight capacity allows for the transport of even the heaviest machinery in a single trip, reducing logistics costs and improving efficiency.
Legal Compliance
The low deck height of lowboy trailers is crucial for legal compliance:
- Allows for the transport of tall equipment without exceeding height restrictions
- Reduces the need for route surveys and special permits in many cases
- Minimizes the risk of accidents due to low clearances
By facilitating legal transport of oversized loads, lowboys help avoid costly fines and project delays.
Loading and Unloading Efficiency
Lowboy trailers often feature design elements that enhance loading and unloading:
- Removable goosenecks for front loading
- Hydraulic ramps or beaver tails for rear loading
- Low approach angles for easy equipment access
These features reduce loading time and minimize the need for additional loading equipment, improving overall operational efficiency.
Stability and Safety
The design of lowboy trailers contributes to enhanced stability and safety during transport:
- Low center of gravity reduces the risk of tipping
- Even weight distribution across multiple axles improves handling
- Robust construction withstands the stresses of heavy loads
These safety features are crucial when transporting valuable and potentially dangerous heavy equipment.
Customization Options
Lowboy trailers can be customized to meet specific transport needs:
- Adjustable axles for weight distribution
- Extendable decks for longer loads
- Specialized tie-down points for secure cargo fastening
This adaptability allows lowboys to handle a wide range of specialized transport requirements.
Cost-Effectiveness
Despite their specialized nature, lowboy trailers offer cost-effective solutions for heavy equipment transport:
- Reduced need for height reduction measures on equipment
- Fewer permit requirements compared to other trailer types for tall loads
- Ability to transport multiple pieces of equipment in a single trip
These factors contribute to lower overall transport costs for heavy machinery.
Industry Recognition
The heavy equipment transport industry widely recognizes the value of lowboy trailers:
- Preferred choice for many heavy haul companies
- Standard equipment for construction and industrial logistics firms
- Often specified in transport contracts for large projects
This widespread adoption underscores the lowboy’s status as a workhorse in the industry.
In conclusion, lowboy trailers are considered the workhorses of heavy equipment transport due to their unique combination of low deck height, high weight capacity, versatility, and efficiency. Their ability to safely and legally transport a wide range of heavy machinery while minimizing logistical challenges makes them indispensable in various industries. As the demand for heavy equipment transport continues to grow, the importance of lowboy trailers in facilitating efficient and compliant transportation is likely to remain paramount.
What advantages do flatbed and step deck trailers offer for heavy hauling?
Flatbed and step deck trailers, while not specifically designed for heavy equipment transport like lowboys, offer distinct advantages that make them valuable options in certain heavy hauling scenarios. These trailers provide flexibility, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness that can be beneficial for specific types of loads and transport requirements.
Flatbed Trailers

Flatbed trailers are characterized by their simple, flat deck without sides or a roof. This basic design offers several advantages for heavy hauling:
Versatility
Flatbeds can accommodate a wide variety of load types:
- Construction materials
- Palletized goods
- Machinery with lower profiles
- Oddly shaped equipment that doesn’t fit well on specialized trailers
This versatility makes flatbeds a cost-effective option for companies that transport diverse cargo types.
Easy Loading and Unloading
The open design of flatbeds allows for:
- Loading and unloading from all sides
- Use of forklifts or cranes for efficient cargo handling
- Quick turnaround times at loading and unloading sites
This accessibility can significantly reduce overall transport time and labor costs.
Cost-Effectiveness
Flatbed trailers are generally less expensive than specialized heavy equipment trailers:
- Lower initial purchase cost
- Reduced maintenance expenses due to simpler design
- Lower operating costs due to lighter weight
For companies that occasionally transport heavy equipment alongside other cargo types, flatbeds can be a more economical choice.
Availability
Flatbed trailers are widely available:
- Common in most trucking fleets
- Easily rented or leased for short-term needs
- Readily available for backhauls, reducing empty miles
This availability can be advantageous when scheduling tight transport deadlines.
Step Deck Trailers
Step deck trailers, also known as drop deck trailers, feature two deck levels, with the lower deck providing additional vertical clearance. This design offers several benefits for heavy hauling:
Increased Vertical Clearance
The lower deck section allows for taller loads:
- Can accommodate equipment up to 10 feet tall without exceeding legal height limits
- Reduces the need for height permits in many cases
- Allows for transport of taller machinery that wouldn’t fit on a standard flatbed
This increased clearance makes step decks suitable for a wider range of heavy equipment.
Easier Loading and Unloading
The “step” design facilitates easier access:
- Lower deck height reduces the angle of approach for loading
- Can often be loaded using ramps rather than cranes
- Allows for drive-on loading of wheeled or tracked equipment
These features can simplify loading procedures and reduce the need for specialized loading equipment.
Weight Distribution
The design of step deck trailers can aid in proper weight distribution:
- Lower center of gravity improves stability
- Weight can be strategically placed on different deck levels
- Some models feature sliding axles for fine-tuning weight distribution
Proper weight distribution is crucial for safe and legal heavy equipment transport.
Versatility
Step decks offer a balance between specialized and general-purpose trailers:
- Can handle both oversized equipment and standard freight
- Suitable for a variety of industries including construction, agriculture, and manufacturing
- Often equipped with multiple tie-down points for secure cargo fastening
This versatility makes step decks a popular choice for companies with diverse transport needs.
Comparative Advantages
To illustrate the specific advantages of flatbed and step deck trailers in heavy hauling, consider the following comparison table:
| Feature | Flatbed | Step Deck | Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deck Height | 58-62 inches | Upper: 58-62 inches, Lower: 36-40 inches | Step Deck for taller loads |
| Load Accessibility | All sides | All sides, plus easier rear access | Both offer good accessibility |
| Typical Length | 48-53 feet | 48-53 feet | Similar, with some variation |
| Legal Height Limit | 8.5 feet from deck | 10 feet from lower deck | Step Deck for taller equipment |
| Typical Weight Capacity | 48,000-60,000 lbs | 48,000-60,000 lbs | Similar, varies by configuration |
| Versatility | Highly versatile | Very versatile, better for taller loads | Both are versatile, with Step Deck having an edge for height |
| Cost | Lower | Slightly higher | Flatbed for budget-conscious operations |
| Availability | Widely available | Commonly available | Flatbed slightly more common |
While both flatbed and step deck trailers offer advantages for heavy hauling, the choice between them often depends on the specific requirements of the load and the transport operation. Flatbeds excel in situations where maximum flexibility and cost-effectiveness are priorities, and the equipment being transported fits within standard height limits. Step decks shine when dealing with taller equipment or when a lower loading height is beneficial.
In conclusion, flatbed and step deck trailers offer significant advantages for heavy hauling in terms of versatility, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. While they may not be suitable for all types of heavy equipment transport, particularly for extremely large or heavy machinery, they provide valuable options for a wide range of heavy hauling scenarios. Their ability to handle diverse cargo types and their widespread availability make them important tools in the heavy transport industry, complementing more specialized trailers like lowboys in creating a comprehensive heavy hauling solution.
When should specialized trailers like double drop and RGN be used?
Specialized trailers such as double drop and Removable Gooseneck (RGN) trailers play crucial roles in the heavy equipment transport industry. These trailers are designed to handle specific challenges that standard trailers cannot address effectively. Understanding when to use these specialized trailers is essential for ensuring safe, legal, and efficient transport of oversized and overweight loads.
Double Drop Trailers
Double drop trailers, also known as double lowboy trailers, feature a well in the middle section that sits lower than both the front and rear decks. This unique design offers several advantages for specific transport scenarios.
When to Use Double Drop Trailers:
Extra Tall Equipment
Double drop trailers are ideal for transporting extremely tall equipment:
- Machinery that exceeds theWhen to Use Double Drop Trailers:
Extra Tall Equipment
Double drop trailers are ideal for transporting extremely tall equipment:
- Machinery that exceeds the legal height limits for standard trailers.
- Examples include large cranes, industrial boilers, and oversized construction equipment.
Heavy Loads
These trailers can handle substantial weight while maintaining stability:
- They typically have a weight capacity ranging from 40,000 to 80,000 pounds.
- The low deck design helps distribute weight evenly across multiple axles.
Legal Compliance
Double drops help avoid legal complications associated with height restrictions:
- The lower center of gravity reduces the risk of exceeding height limits.
- This can eliminate the need for special permits in many cases, streamlining the transport process.
Complex Loads
Double drop trailers are well-suited for complex load configurations:
- The well design allows for better load placement and stability.
- They can accommodate equipment with varying dimensions and shapes.
Removable Gooseneck (RGN) Trailers
RGN trailers are characterized by their detachable front section, which can be lowered to ground level. This feature allows for easy loading and unloading of heavy machinery.
When to Use RGN Trailers:
Self-Loading Equipment
RGN trailers are particularly beneficial for equipment that can be driven onto the trailer:
- Ideal for large tractors, mobile cranes, and certain types of construction machinery.
- The ability to drive onto the trailer eliminates the need for additional loading equipment.
Heavy and Oversized Loads
RGN trailers can accommodate extremely heavy loads:
- They often have a weight capacity exceeding 150,000 pounds.
- This makes them suitable for transporting massive industrial machinery or components.
Height Restrictions
The low deck height of RGN trailers allows for taller loads:
- Can transport equipment that exceeds standard height limits without requiring special permits.
- This is especially useful in regions with strict height regulations.
Complex Transport Needs
RGN trailers offer versatility in handling various transport scenarios:
- The detachable gooseneck allows for flexible loading configurations.
- They can be adjusted to accommodate different load lengths and widths.
| Trailer Type | Best Suited For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Double Drop | Extra tall loads | Low well design for height clearance |
| RGN | Self-loading equipment | Detachable gooseneck for easy access |
In summary, specialized trailers like double drop and RGN are essential tools in heavy equipment transport. Double drop trailers excel in handling extra tall loads while ensuring legal compliance and stability. RGN trailers are ideal for self-loading equipment and exceptionally heavy or oversized loads. Understanding when to use these specialized trailers can significantly enhance the efficiency and safety of heavy hauling operations.
What legal considerations and permits are required for heavy equipment hauling?
Transporting heavy equipment involves navigating a complex landscape of legal considerations and permit requirements. Compliance with these regulations is crucial to ensure safe operations and avoid costly penalties.

Weight Limits
Each state has specific weight limits for vehicles operating on public roads. These limits typically include:
- Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR): The total weight of the vehicle plus its cargo.
- Axle Weight Limits: Maximum weight allowed on each axle.
Exceeding these limits can lead to fines, damage to road infrastructure, and increased risk of accidents.
Height Restrictions
Legal height limits vary by jurisdiction but generally range from 13’6″ to 14’0″. Transporting loads that exceed these heights may require:
- Special Permits: Often referred to as “oversize load permits.”
- Route Surveys: To identify potential obstacles such as bridges or power lines.
Ensuring compliance with height regulations is essential to avoid accidents and legal issues during transport.
Width Restrictions
Most states impose width limits on vehicles transporting cargo. Standard width limits are typically set at 8’6″. Loads exceeding this width may require:
- Escort Vehicles: To guide the transport vehicle through narrow or congested areas.
- Special Permits: Similar to height permits, these may be required for wide loads.
Adhering to width regulations helps ensure safe passage through roadways and urban areas.
Specialized Permits
Certain types of heavy equipment may require additional permits beyond standard oversize load permits. Examples include:
- Superload Permits: For extremely heavy or oversized loads that exceed typical limits.
- Seasonal Permits: Some jurisdictions impose seasonal weight restrictions during certain months (e.g., spring thaw).
Understanding the specific permit requirements based on load type and route is essential for compliance.
Insurance Requirements
Transporting heavy equipment often necessitates specialized insurance coverage. Key considerations include:
- Liability Insurance: Protects against damages caused during transport.
- Cargo Insurance: Covers loss or damage to the transported equipment.
Verifying insurance requirements with local authorities is crucial before commencing transport operations.
State-Specific Regulations
Each state has its own set of regulations governing heavy equipment transport. Key considerations include:
-
Permit Application Processes: Vary by state; some states allow online applications while others require in-person submissions.
-
Local Ordinances: Some municipalities may have additional restrictions or requirements beyond state laws.
Staying informed about state-specific regulations is vital to ensure compliance throughout the transport process.
| Legal Consideration | Description | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Weight Limits | Maximum weight allowed on vehicles | Fines, road damage |
| Height Restrictions | Legal height limits for loads | Accidents, fines |
| Width Restrictions | Maximum width allowed on vehicles | Escort requirements |
| Specialized Permits | Additional permits for oversized loads | Delays, fines |
| Insurance Requirements | Necessary coverage for liability and cargo | Financial risk |
In conclusion, navigating the legal landscape of heavy equipment hauling requires careful attention to weight limits, height restrictions, width limitations, specialized permits, and insurance requirements. Ensuring compliance with these regulations not only enhances safety but also protects against potential legal repercussions. Transporters must stay informed about state-specific laws and adapt their operations accordingly to facilitate smooth and compliant heavy hauling activities.
How can proper securement techniques ensure safe heavy equipment transport?
Proper securement techniques are critical in ensuring the safe transportation of heavy equipment. Inadequate securement can lead to accidents, damage to cargo, or injuries during transit. Implementing effective securement practices enhances safety and compliance with regulatory standards.
Understanding Securement Principles
Securement involves using appropriate methods and materials to prevent movement of cargo during transit. Key principles include:
-
Weight Distribution: Properly distributing weight across the trailer helps maintain stability during transport.
-
Tie-down Techniques: Using appropriate tie-down methods ensures that cargo remains securely fastened throughout the journey.
-
Equipment Compatibility: Selecting securement devices that match the specific type of equipment being transported is essential for effective restraint.
Types of Securement Devices
Several securement devices are commonly used in heavy equipment transport:
-
Chains: Heavy-duty chains provide strong restraint but require proper tensioning techniques.
-
Straps: Ratchet straps offer flexibility in securing various types of machinery while maintaining tension throughout transit.
-
Dunnage: Wooden blocks or pads used under equipment prevent shifting during transport by providing a stable base.
Load Configuration
The configuration of the load plays a significant role in securement effectiveness:
-
Center of Gravity: Positioning heavier items closer to the trailer’s center improves stability.
-
Multiple Tie-down Points: Utilizing multiple tie-down points around the load distributes forces evenly during transit.
-
Avoid Overhangs: Ensuring that no part of the load extends beyond the trailer’s edges minimizes risks associated with shifting or tipping.
Regulatory Compliance
Securement practices must comply with federal and state regulations governing cargo securement. Key guidelines include:
-
Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) Standards: These standards outline specific requirements for securing different types of cargo, including heavy machinery.
-
State Regulations: Some states may have additional requirements regarding securement practices; staying informed about local laws is crucial.
-
Inspection Protocols: Regularly inspecting securement devices before departure ensures they are in good condition and capable of handling expected forces during transit.
| Securement Device | Description | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Chains | Heavy-duty restraint devices | Large machinery |
| Ratchet Straps | Flexible straps with tensioning mechanisms | Various cargo types |
| Dunnage | Stabilizing blocks/pads under equipment | Prevents shifting |
In summary, proper securement techniques are essential for ensuring safe transportation of heavy equipment. By understanding securement principles, utilizing appropriate devices, configuring loads effectively, and adhering to regulatory standards, transporters can significantly reduce risks associated with cargo movement during transit. Prioritizing securement not only protects valuable machinery but also enhances overall safety on the roadways.
What factors should be considered when choosing the right trailer for specific equipment?
Selecting the right trailer for transporting specific types of heavy equipment involves careful consideration of various factors that influence safety, efficiency, and compliance with regulations. Understanding these factors ensures that logistics operations run smoothly while minimizing risks associated with transporting oversized loads.
Equipment Characteristics
The first step in choosing an appropriate trailer is assessing the characteristics of the equipment being transported:
-
Weight: Determine the total weight of the machinery along with any attachments or accessories that will be transported alongside it. This will help identify a trailer with sufficient weight capacity.
-
Dimensions: Measure the length, width, and height of the equipment accurately. Understanding these dimensions will guide you in selecting a trailer that meets legal size restrictions while accommodating your load comfortably.
-
Loading Method: Consider how the equipment will be loaded onto the trailer—whether it will be driven on (self-loading) or requires ramps or cranes for loading/unloading purposes.
-
Type of Equipment: Different types of machinery may have unique requirements based on their design (e.g., tracked vs wheeled), which influences trailer selection (e.g., lowboy vs flatbed).
Legal Considerations
Compliance with legal regulations is paramount when selecting a trailer:
-
Weight Limits: Ensure that both individual axle weights and gross vehicle weights comply with local laws; exceeding these limits may result in fines or permit requirements.
-
Height Regulations: Verify that selected trailers allow your load’s height to remain within legal limits; this may dictate whether you need a lowboy or double drop trailer instead of a standard flatbed.
-
Width Restrictions: Confirm whether your load exceeds standard width limitations; if so, you may need escort vehicles or special permits depending on local laws governing oversized loads.
-
Permit Requirements: Research any necessary permits based on your route; some jurisdictions require advance notice or specific approvals before transporting oversized loads through their areas.
Operational Efficiency
Selecting a trailer that enhances operational efficiency contributes significantly to successful logistics operations:
-
Loading/Unloading Time: Choose a trailer design that facilitates quick loading/unloading processes—this minimizes downtime at job sites where time is money!
-
Maneuverability Needs: Assess how easily you’ll need to navigate tight spaces during transport; some trailers offer better maneuverability than others based on their length/width ratios—consider this when planning routes!
-
Fuel Efficiency Considerations: Heavier trailers often result in higher fuel consumption; selecting lighter models where feasible can help reduce overall transportation costs over time!
-
Availability & Rental Options: If you don’t own specialized trailers outright consider rental options—this flexibility allows you access without long-term commitments while still meeting project demands!
-
**Maintenance History & Condition: Regularly inspect any used trailers before purchase/rental—ensure they’re well-maintained & capable of handling expected loads safely!
| Factor | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Equipment Weight | Total weight including attachments |
| Dimensions | Length, width & height measurements |
| Loading Method | Self-loading vs crane-assisted loading |
| Legal Compliance | Adherence to weight/height/width laws |
| Operational Efficiency | Loading/unloading time & maneuverability |
In conclusion, choosing the right trailer for specific heavy equipment requires careful consideration of various factors including characteristics of the load itself as well as legal compliance issues related transportation regulations! By evaluating these elements thoroughly before making decisions about which type(s) best suit your needs—you’ll ensure safer more efficient logistics operations overall!
How does regular maintenance impact the performance of heavy equipment trailers?
Regular maintenance plays a vital role in ensuring optimal performance and longevity for heavy equipment trailers used in transportation logistics operations! Neglecting maintenance can lead not only costly repairs down-the-line but also potential safety hazards during transit! Understanding how routine upkeep affects performance helps operators maximize efficiency while minimizing risks associated with hauling valuable machinery!
Importance Of Regular Inspections
Conducting regular inspections forms an integral part-of any effective maintenance program! Inspections should focus-on key components such as brakes tires suspension systems lights wiring connections among others! Identifying issues early-on allows operators address them proactively rather than waiting until problems escalate into major failures!

Enhancing Safety
Regular maintenance directly contributes-to improved safety measures when transporting heavy loads! Well-maintained brakes ensure reliable stopping power reducing chances accidents occurring due-to malfunctioning parts! Similarly properly inflated tires enhance traction stability improving overall handling characteristics while driving under varying conditions!
Reducing Downtime
Routine maintenance minimizes downtime associated-with unexpected breakdowns! By addressing minor issues before they develop into major problems operators avoid costly delays caused by repairs needing extensive timeframes! Scheduling regular service intervals helps keep fleets operational ensuring projects remain on track without interruptions!
Extending Trailer Lifespan
Investing-in regular upkeep extends lifespan significantly reducing replacement costs over time! Components like axles suspensions frames wear down naturally; however proactive measures such as lubrication inspections replacements when necessary prolong their usability avoiding premature failures!
Improving Fuel Efficiency
Well-maintained trailers operate more efficiently translating into lower fuel consumption rates! For example properly aligned wheels reduce rolling resistance allowing vehicles travel farther per gallon consumed! Keeping tires inflated correctly also impacts mileage positively—ensuring operators get maximum value from every trip taken!
Compliance With Regulations
Many jurisdictions mandate regular inspections & maintenance records as part-of compliance efforts surrounding commercial vehicle operations! Failing adhere these guidelines could result fines penalties impacting profitability negatively! Maintaining accurate documentation demonstrates commitment-to safety responsible operation enhancing reputation within industry!
Cost Savings Over Time
While regular maintenance incurs upfront costs it ultimately saves money long-term by preventing expensive repairs replacements down-the-line! Investing-in preventive measures yields significant returns through reduced operational costs improved reliability overall satisfaction among clients relying-on timely deliveries!
In summary regular maintenance significantly impacts performance longevity safety aspects related-to heavy equipment trailers used within transportation logistics sectors! By prioritizing routine inspections addressing minor repairs proactively operators maximize efficiency minimize risks associated-with hauling valuable machinery effectively contributing success projects undertaken across various industries!
This concludes your article draft titled “What kind of trailer hauls heavy equipment,” covering all specified sections comprehensively while adhering strictly-to outlined requirements!